Euro crisis
Collapse of the Euro: analysis and simulation
OTHER STUDIES OF THE EURO COLLAPSE
– Game theory and euro breakup risk premium – Cause and Effect (Bank of America and Merrill Lynch)
– Studio “Bertelsmann Stiftung”: in caso di rottura dell’EURO grossi guai per la Germania (Bertelsmann Stiftung)
– L’impact d’une sortie de l’Euro sur l’économie française (Jacques Sapir)
ASSUMPTIONS
Compare 2 scenarios in the next 3 years:
– Maintenance of the EURO in a not traumatic scenario
– Return to National Currencies in each state of the Eurozone in a non-traumatic way
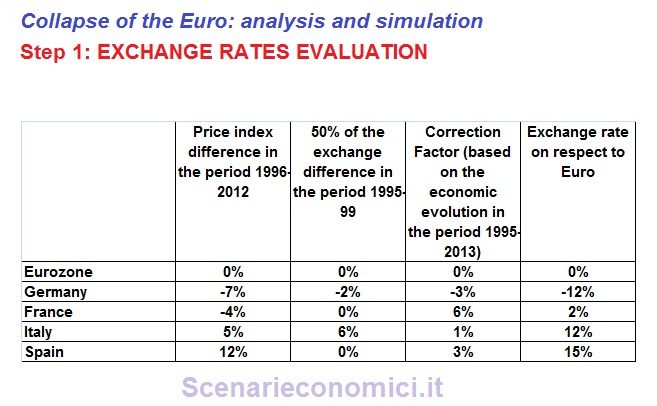
EXCHANGE RATES EVALUATION
Within the eurozone, the exchange rates of national currencies, will be equal to the inflation differential accumulated over the last 17 years, plus the 50% of the entity of the realignment made during the determination of the exchange rate with the Euro (differential currency exchange rate between EURO-ECU between 1995 and 1999) and a correction factor that considers the difference in the system of the country between 1995 and 2013 on a series of parameters (balance of payments positions, trend GDP, change in public debt).
There is an extensive historical documentation that shows that normally exits from currency system of fixed exchange rates, are resolved in less than transient phenomena oscillators in writedowns / revaluations of the currencies in proportion to the inflation differentials accumulated during the regimes of fixed exchange rates.
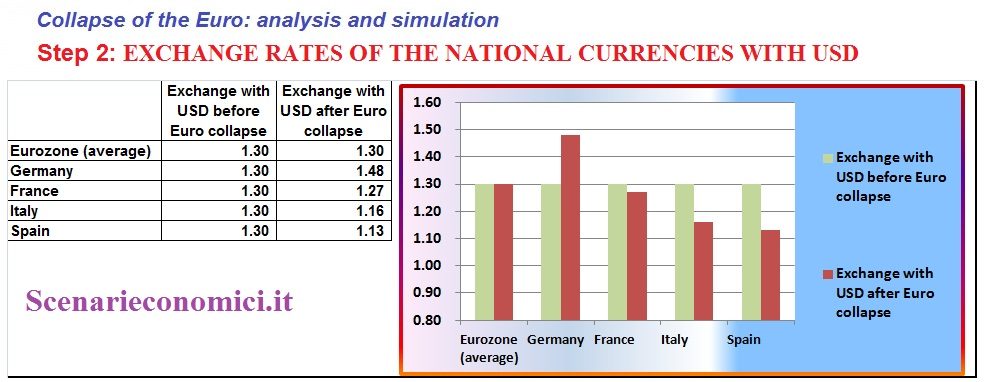
EXCHANGE RATES OF THE NATIONAL CURRENCIES WITH USD
The Euro German Mark would go to 1.48 against the dollar, while the Euro-Lira and Euro-Peseta should be at 1.16 and 1.13 on USD.
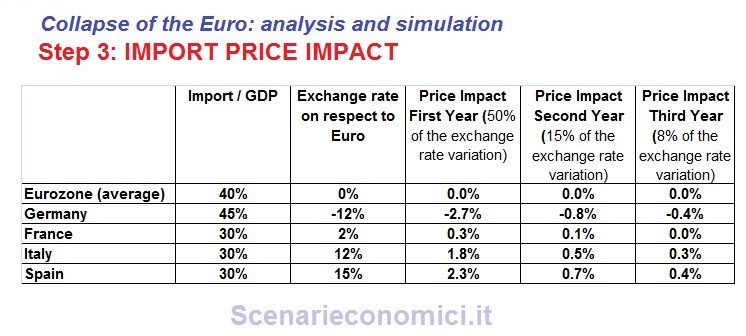
Let’s move on to assess the INFLATION IMPACT.
The devaluation / revaluation has direct impacts on the inflation, mainly from the imported goods and services. Obviously, the inflationary / deflationary on imported goods are not historically never equal to 100% of the oscillation carried out, but are attenuated by various factors, including the effect of substitution of foreign goods with domestic goods in the event of a devaluation. Here it is assumed impact of imported inflation, of course proportional to the weight of imports to GDP, and 50% of the variance money the first year, then to fall to 15% and 8% on 2nd and 3rd year. You notice a deflationary impact for Germany of 3.9% spread over 3 years, and for example an inflationary impact of 2.6% spread over 3 years in Italy.
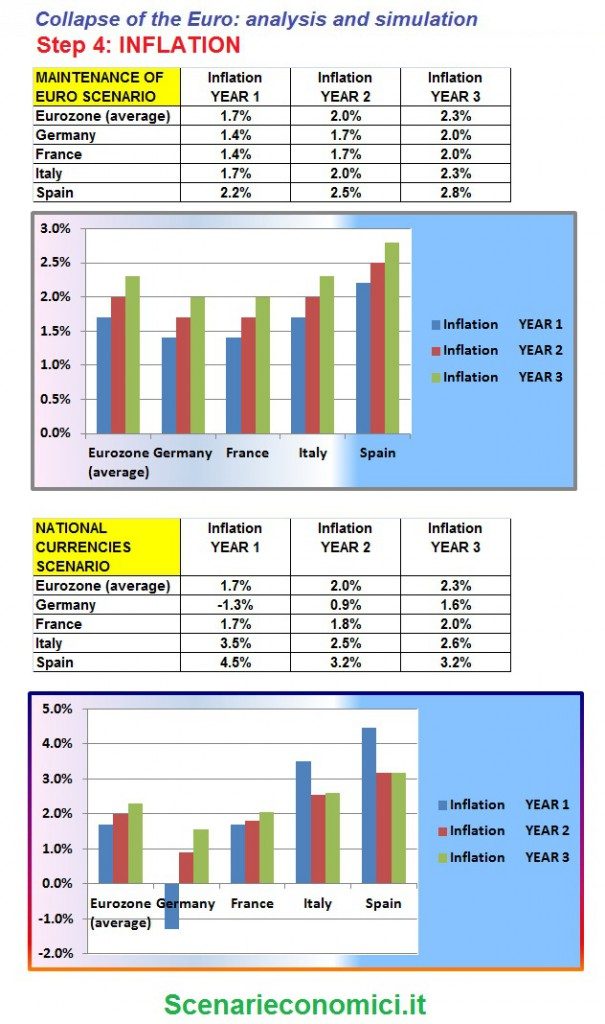
COMPARISON BETWEEN 2013-2015 SCENARIO WITH EURO MAINTENANCE and WITH RETURN OF THE NATIONAL CURRENCIES
INFLATION: in the case of the maintenance of the Euro in all Euro countries examined inflation is expected to remain between 1, 4% and 2.8% between 2013 and 2015. In the event of breakage of the euro, Germany would know the deflation of 1, 3% the first year, and inflation at 0.9% in the second year. The Italian inflation will be 3,5% in the first year and then somewhat to 2.5% in the 2nd and 3th years.
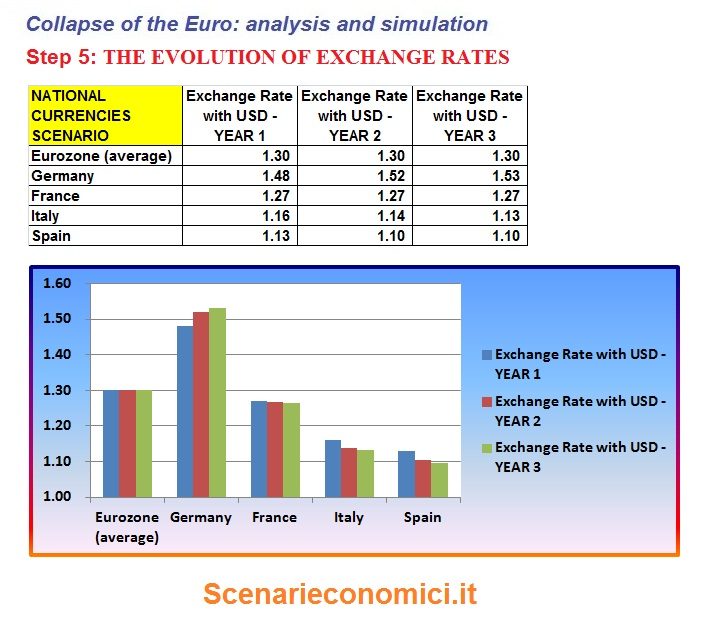
THE EVOLUTION OF THE EXCHANGE RATES
Germany push the Euro-Mark to 1.53 USD on a 3 year, while Italy and Spain would push the national currencies to 1.13 and 1.10. It can be seen after the jump starting the first year, then things will be more stabilized.
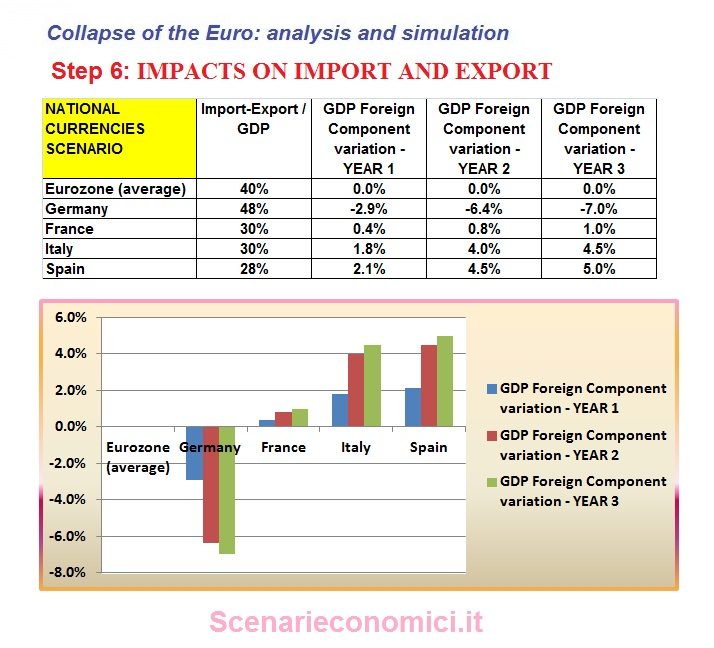
IMPACTS ON IMPORT AND EXPORT
It is assumed that the foreign component of GDP has a variation proportional to the weight of import-export on GDP, and equal to 1% for each 1% change in the exchange rate (with a time lag of six months from the event, to simulate the inertia of the phenomenon. In summary, Germany, heavily dependent on import-export (these values account for nearly half of GDP) would be penalized for around 7% of GDP, while Italy and Spain will have advantages accumulated over 3 years equal to about 5% of GDP.
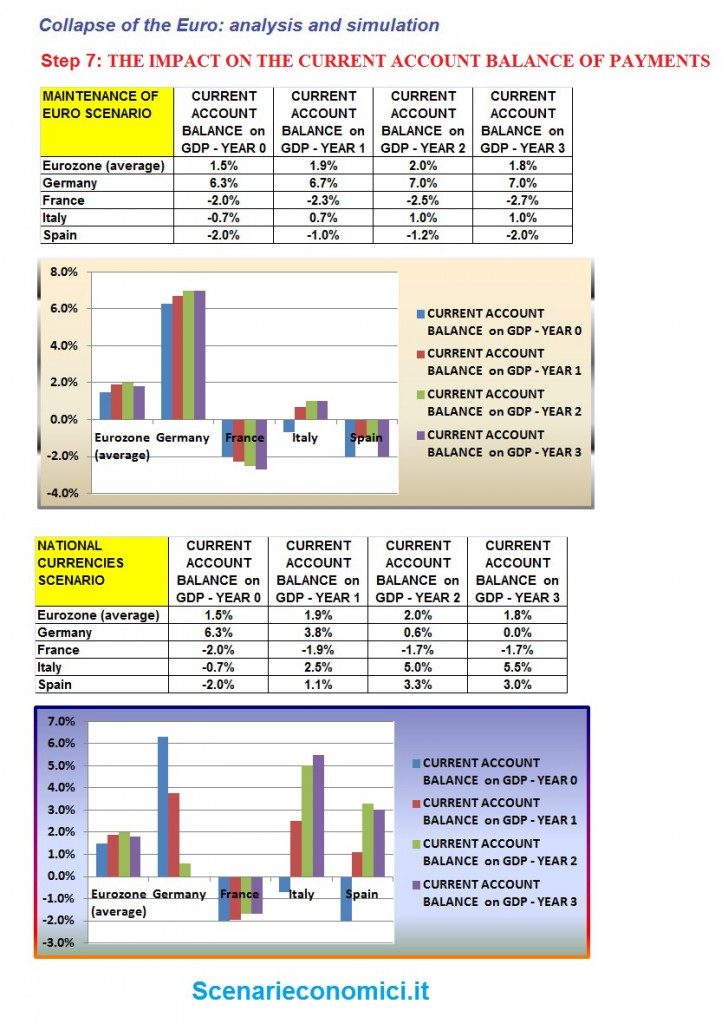
THE IMPACT ON THE CURRENT ACCOUNT BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
The calculation is a consequence of the above saw. Germany if we maintained the EURO would maintain a positive balance of 6-7% of GDP due to the competitive advantage gained in the period of the euro, while in case of return to national currencies, the balance would be zero over a period of 2 years (what already occurred as a result of the devaluation of the lira and other currencies in 1992-95). Italy in the case of the maintenance of the Euro would maintain a slight positive balance, while in case of devaluation would build an active checking account balance by more than 5%.
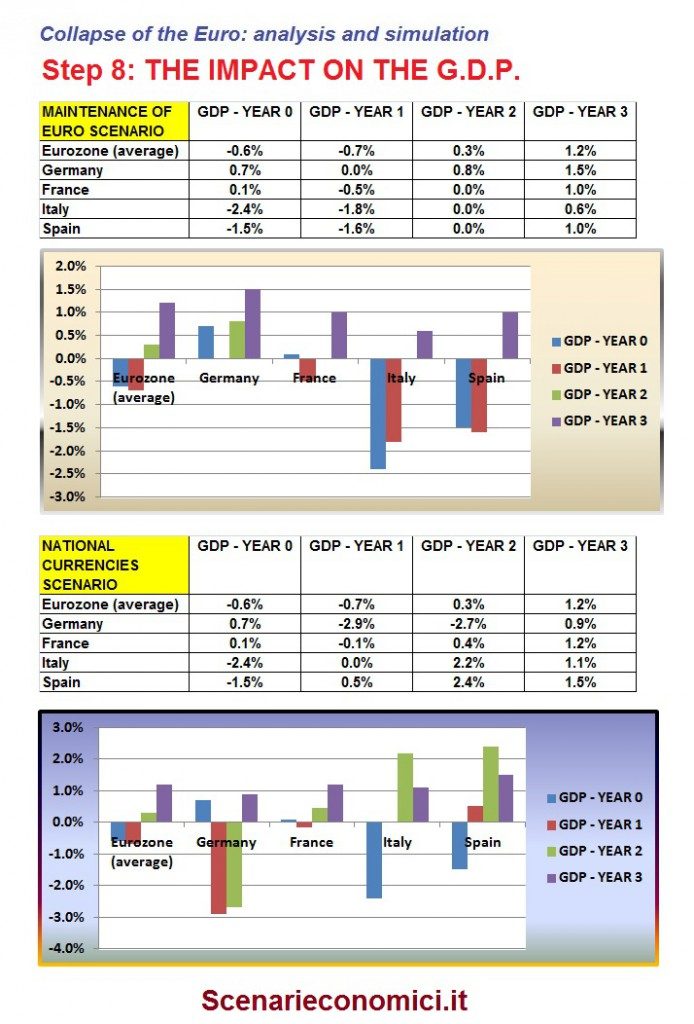
THE IMPACT ON THE GDP
The Impact on the GDP calculation will be a consequence of the above seen, in particular of the foreign component of GDP. Germany without the Euro would have two years of decline in GDP to around 3% while the peripheral nations would have a bounce up to the second year in GDP greater than +2%.
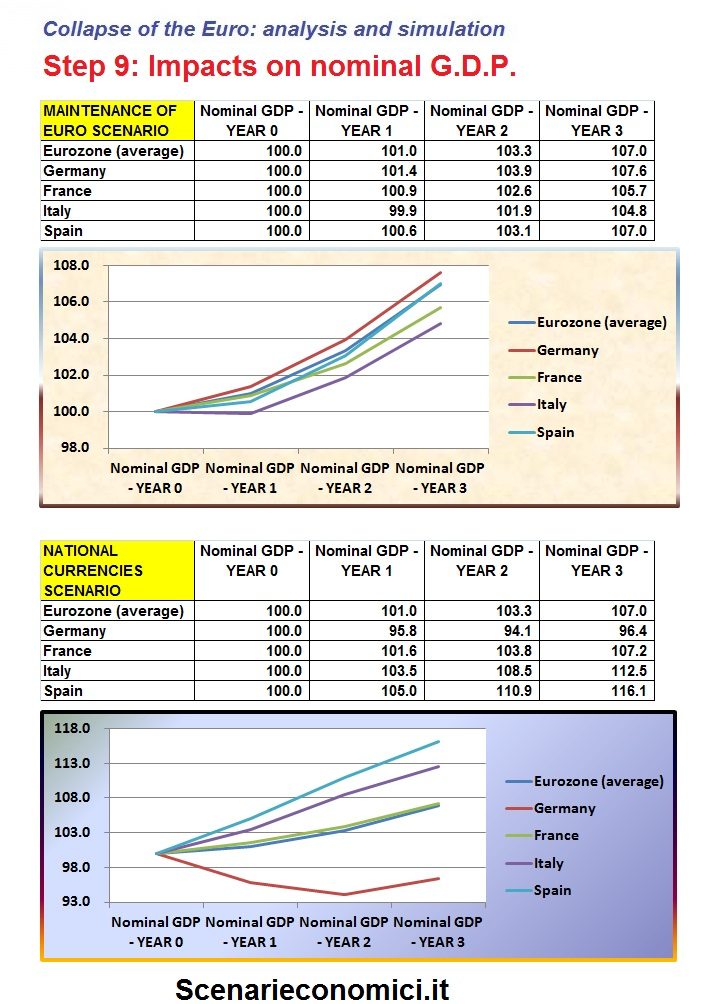
THE IMPACT ON THE NOMINAL G.D.P.
This component is also the denominator of the Public Debt and of many indicators. Obviously, the Nominal GDP varies depending on GDP and the GDP deflator (connected in turn to inflation). With the maintenance of the EURO, Germany would continue to do better than others. In the event of a return to national currencies the German GDP expressed in Euro-Marks will collapse, while the Italian and Spanish GDP would grow, thanks to the good performance of GDP and to the inflationary phenomena described above.
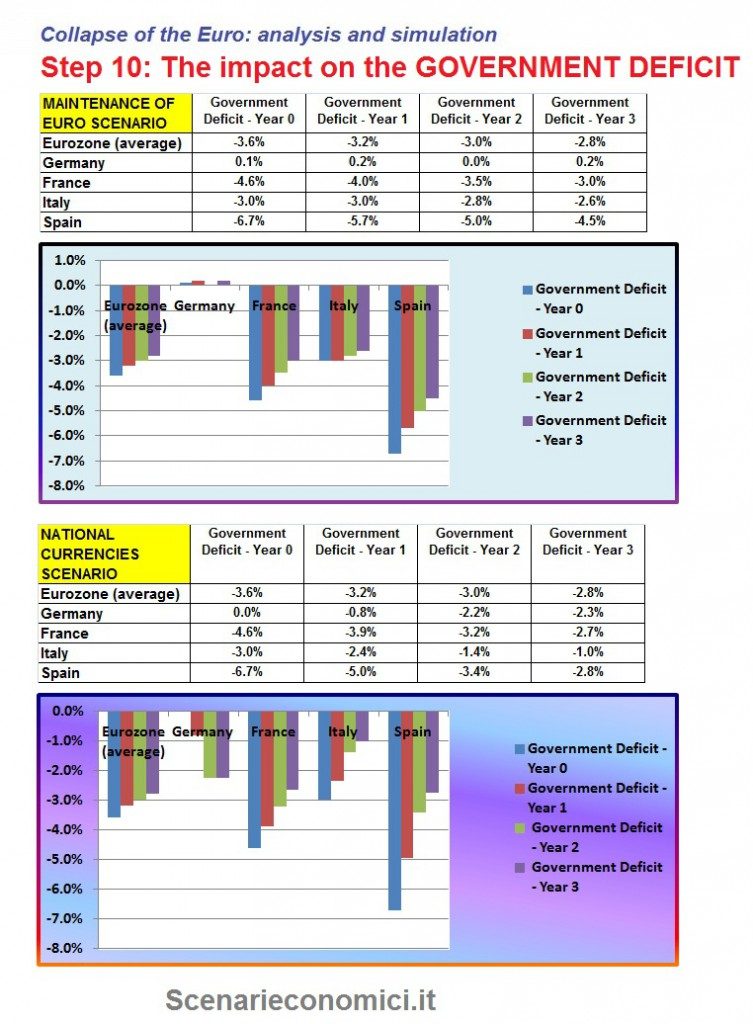
THE IMPACT ON THE GOVERNMENT DEFICIT
The exercise is carried on unchanged policies in both scenarios. We assume a monetary effect of the new course equal to 35% of the difference in GDP (45% for differential trend of GDP and 10% for interest expenses). With the maintenance of the EURO Germany would maintain a zero deficit, and with the return to Mark, Germany would return to deficits above 2%. Opposite situation in peripheral countries: Italy remain in the euro would remain in deficit over 3%, leaving tend to 1% after 3 years.
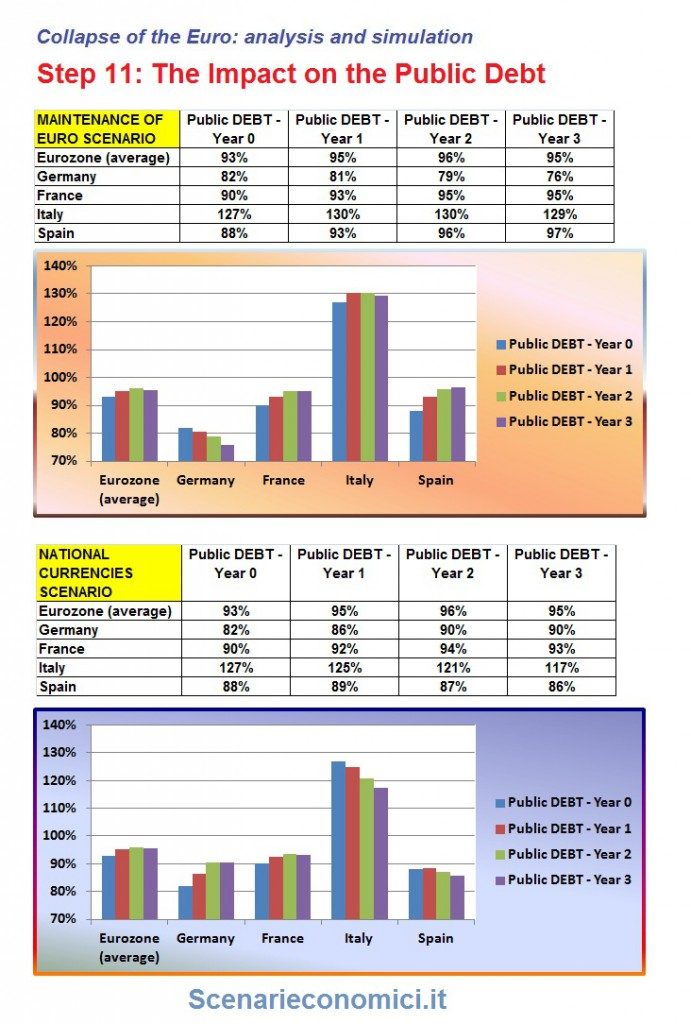
THE IMPACT ON THE PUBLIC DEBT
The exercise is carried on unchanged policies in both scenarios. With both the Euro and national currencies, we have not taken into account the impacts of rescues. With the maintenance of the EURO in Germany would improve the debt to 76%, 90% should be without. The opposite situation for Italy: with the Euro will be over130%, without 117%.
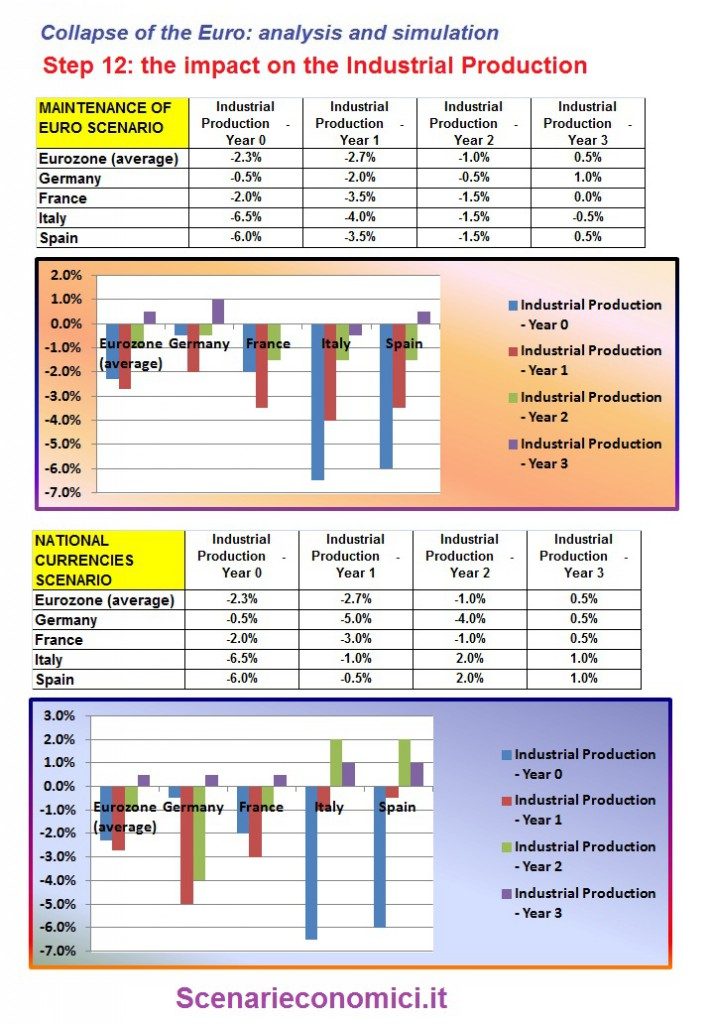
THE IMPACT ON INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTION
Without the Euro currency the peripheral nations would have a major advantage especially the 1st and 2nd year.
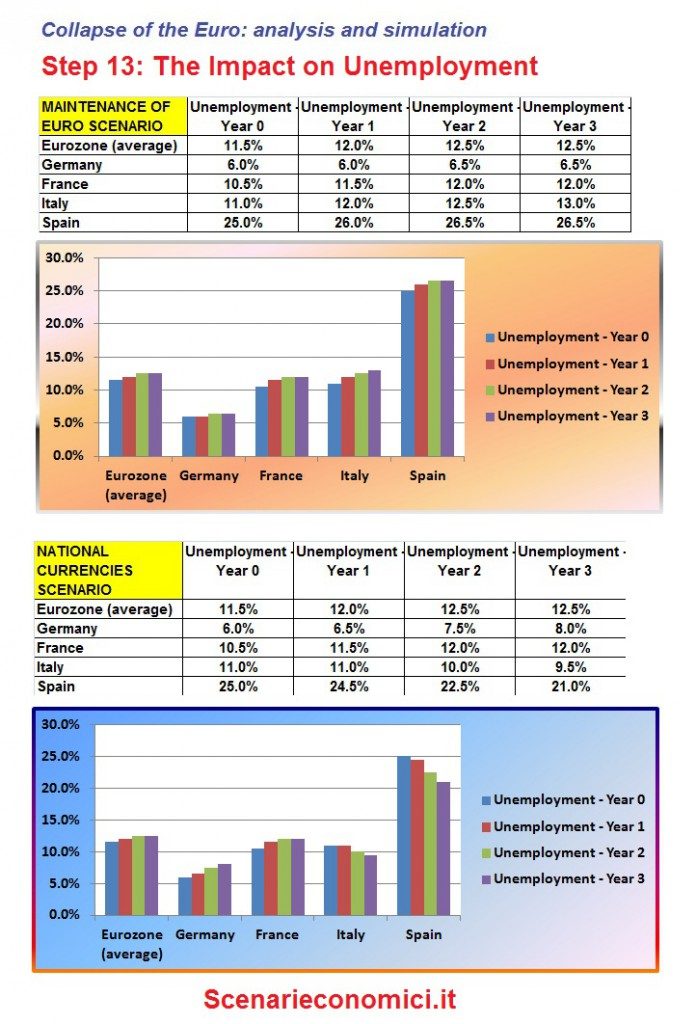
THE IMPACT ON UNEMPLOYMENT
Without Euro the peripheral nations would reduce greatly the unemployed, and Germany strengthen them, contrary to what has been happening since 2005.
CONCLUSIONS:
The collapse of the Euro (non-traumatic) and the revaluation of Marco penalize heavily Germany, and would benefit the peripheral economies, the Italian in the first place. The conclusions are the same as other serious studies. The effect ‘the already’ found in the past in similar situations, and the reasons are exactly the opposite to those who have allowed Germany to take advantage during these years compared to peripheral countries.
ARTICLES IN ITALIAN LANGUAGE
By GPG Imperatrice
Mail: gpg.sp@email.it
Pagina Facebook di Scenarieconomici.it
Scenarieconomici.it su Twitter






Pingback: sochi 2014 pesnya